Sarpa salpa
Diagnosis
Diagnosis_Genus: Sarpa Bonnaparte. Appeared as name only; as a section under *Box* as '96. *Box*, Cuv. (Boops, Riss.). 1. Box, Nob. 2. Sarpa, Nob. in Bonaparte, C.L. (1831). Saggio di una distribuzione metodica degli animali vertebrati, (1831) 78 pp or Giornale Arcadico di Scienze Lettere ed Arti, vol. 52 (1831)
Diagnosis_Species: Sparus salpa Linnaeus. S. cauda bifida, lineis fulvis longitudinalibus utrinque undecim. D. II/28. P. I6. V. 6. A. 3/I7. C. I7. Art. gen. 38. Syn. 60. Sparus lineis utrinque undecim aureis parallelis longitudinalibus. Habitat in M. Mediterraneo.
Body_adults_length_maximum: 51 cm
Body_adults_length_common: 30 cm
Body_juvenile_length: < 21 cm (DORIS)
Body_sexual_maturity_length: 19.5 cm (Criscoli et al., 2006)
Body_egg_length: 0.875-0.985 mm (fisheggs-and-larvae.saiab)
Sequence_Cytb: AF240704 (Chiba et al., 2009), DQ197992 (Meynard et al., 2012)
Sequence_16S: AF247402 (Meynard et al., 2012)
Sequence_Rhod: EF439306 (Meynard et al., 2012)
Sequence_RAG1: HQ676686 (Meynard et al., 2012)
Etymology
The name of the genus “sarpa” comes from the Spanish “salpa” = toad. The name of the species comes from the Latin “salpa” = fish. In short, it is a “toad fish”, probably due to its flesh, without value and toxic during some periods of the year, as well as the secretion from the skin of the toad (http://www.photomazza.com/?Sarpa-salpa&lang=en).
Type species
The type species of the genus Sarpa is Sparus salpa (Linnaeus 1758).
Ecology
Sarpa salpa is a typical fish of temperate and tropical areas like the Mediterranean Sea, the east Atlantic (from the Gascony gulf to South Africa), the west Indian Ocean (from South Africa to southern Mozambique) (Criscoli et al., 2006).
Larvae of Sarpa salpa have a mixed diet which includes copepods and diatoms, young are mainly carnivorous on crustaceans, adults almost exclusively herbivorous (Fishbase, Criscoli et al., 2006).
No sexual dimorphism.
Habitat: seagrass bottom
Habitat: sandy bottom
habitat: coastal
Substrate: water
Sociability_adults: gregarious
Salinity: marine
Salinity: brackish
Depth: 5-70 m (Fishbase)
Oxygen_level: oxic
Temperature: 15-19°C (EOL)
Salinity: 37.15-37.97 PSU (EOL)
Life cycle
Sarpa salpa is a non migratory species.
Reproduction_mode: sexual_hermaphrodite_protandrous
Longevity: more than 3 years (van der Walt & Beckley, 1997)
Generation_time: 1 to 3 years ((DORIS)
Spawning_method: external fertilization in the water column
Fertility_period: seasonal (during Spring, from March to May, Criscoli et al., 2006)
Fertility_period: seasonal (during Autumn, from the end of September to November, Criscoli et al., 2006)
Feeding behaviour
Mode of locomotion
Original description
Reference(s)
Attached phylogeny
Observation site(s)
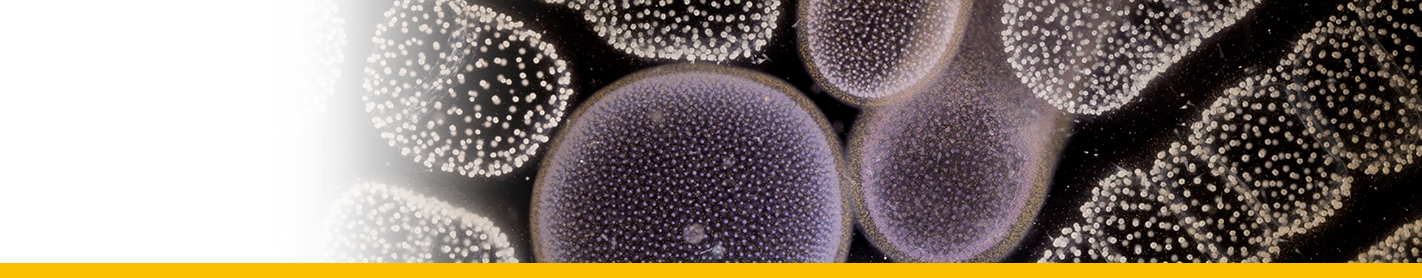
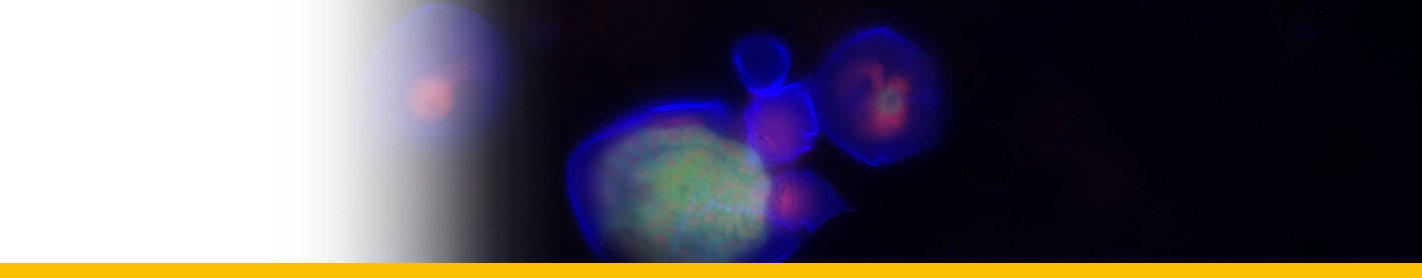
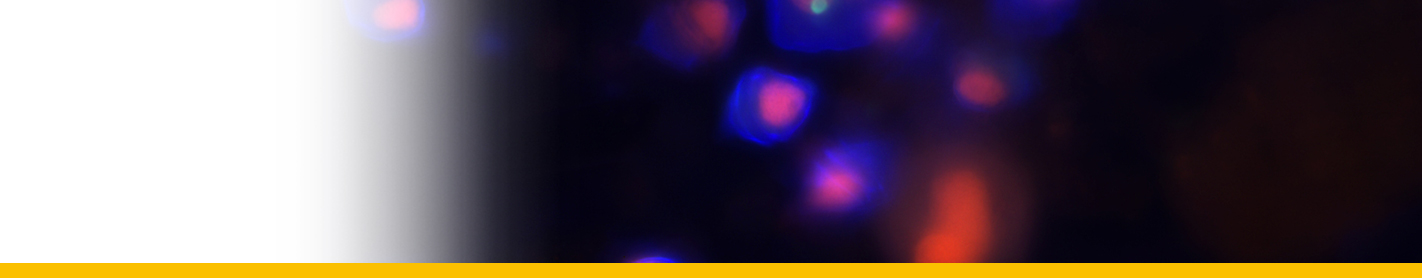
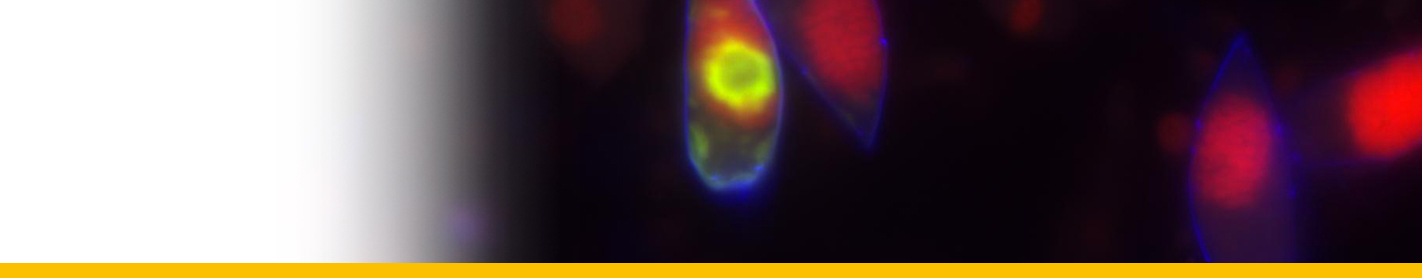
SYMBIONTS
| Association with... | Region origin | Name of site | In reference... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amyloodinium amylaceum | Messine harbor | ||
| Amyloodinium amylaceum | Naples |
(1920) Les péridiniens parasites. Morphologie, Reproduction, Ethologie. . Archives de Zoologie Expérimentale et Générale 59:1-475. |