Dissodinium pseudocalani
Diagnosis
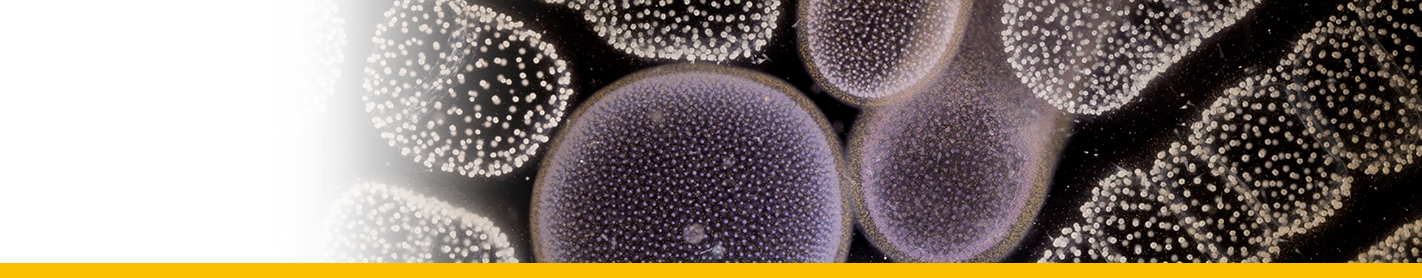
Diagnosis_Genus: Dissodinium Klebs in Pascher, emend. Elbr. & Dreb. 1978. Marine ectoparasitic dinophytes, host: crustacean eggs. Asexual reproduction (sporogenesis) by obligate sequence of primary cysts, secondary cysts, and formation of planospores (dinospores). Primary cyst spherical, with large food vacuole. Nucleus spherical, located in the parietal cytoplasm. Chromatophores present or lacking. Inside the primary cyst wall the protoplast divides by repeated binary fission (palintomy) into 2, 4, 8, 16, or more secondary cysts. The secondary cysts form 5 to 16 or more (rarely less than 5) dinospores. Dinospores small, Gymnodinium- or Gyrodinium-shaped, biflagellate, athecate. The dinospores attach to the host, loose their motility and form a sucker organelle. Hypertrophic growth by phagotrophic uptake of host material. Finally, the growth phase terminates with formation of a primary cyst. No bioluminescence.
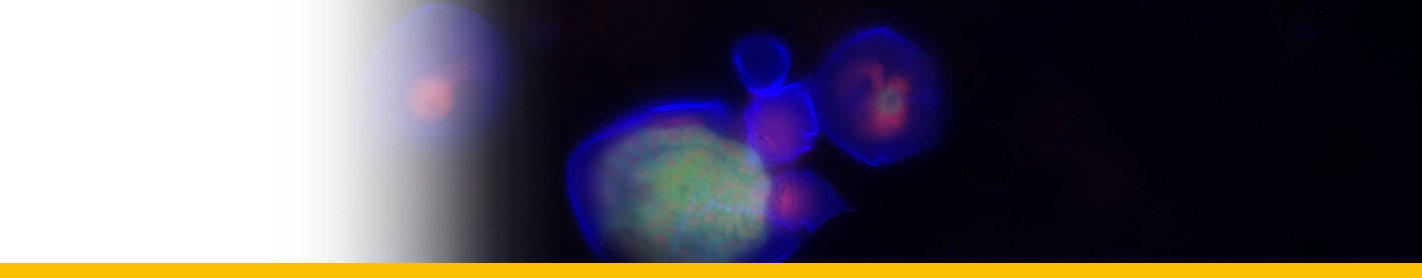
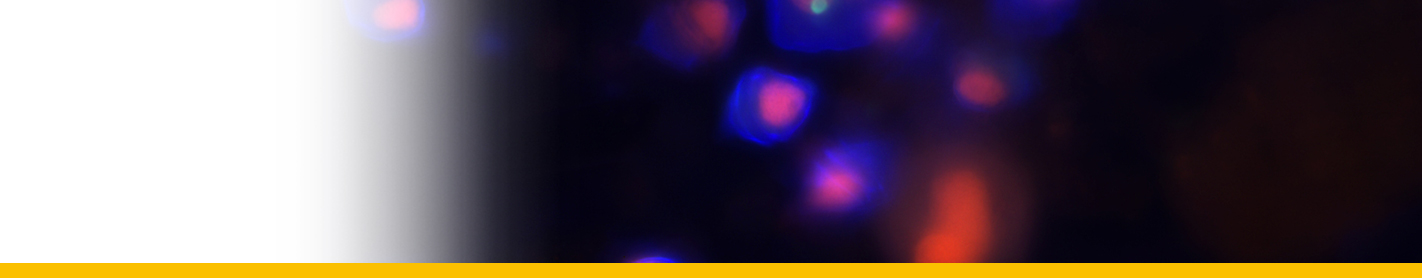
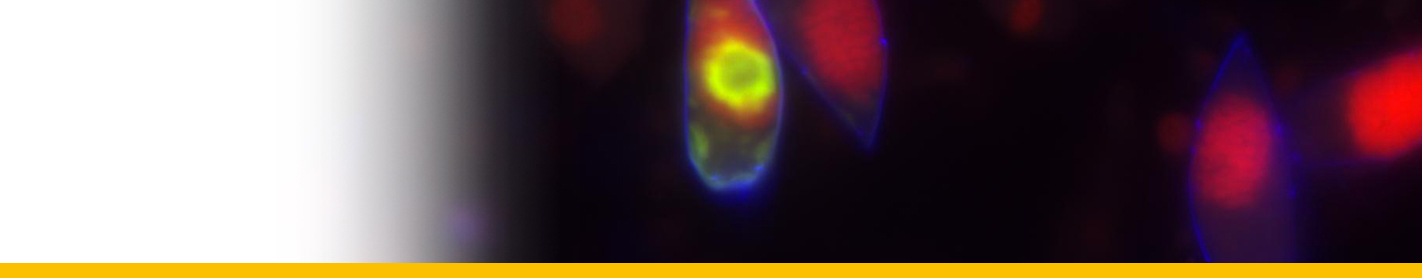
Diagnosis_Species: Dissodinium pseudocalani Drebes 1969. Ectoparasite on eggs of the copepod Pseudocalanus elongatus. The vesicular parasitic stage adheres to the host by a suction organ. After the substrate of the egg is consumed, the parasite develops into a spherical primary cyst which produces 8, 16 or 32 oval secondary cysts by simultaneous cell divisions (palintomic sporogenesis). Each secondary cyst forms 16 or 32 dinospores. The dinospores are colourless, flagellated and of the Gymnodinium-type. During reproduction a large reddish or greenish coloured food source is resorbed by the protoplast and diminishes in size.
Body_trophonts_length: 150-250 µm
Body_spores_length: 15.4-12.6 µm
Etymology
pseudocalani: infected Pseudocalanus elongatus
Type species
The type species for the genus is Dissodinium pseudolunula.
Type illustration / Type locality / Type specimen
Type host: Pseudocalanus elongatus.
Ecology
Substrate: epizoic
Salinity: marine
Life cycle
Generation: <1 month
Reproduction_mode: asexual
Symbiont: horizontal
Feeding behaviour
Mode of locomotion
Reference(s)
Observation site(s)
HOSTS
| Association with... | Region origin | Name of site | In reference... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudocalanus elongatus | Helgoland |
(1969) Dissodinium pseudocalani sp. nov., ein parasitischer Dinoflagellat auf Copepodeneiern. Helgoländer Meeresuntersuchungen 19:58-67. |