Alexandrium fundyense
Diagnosis
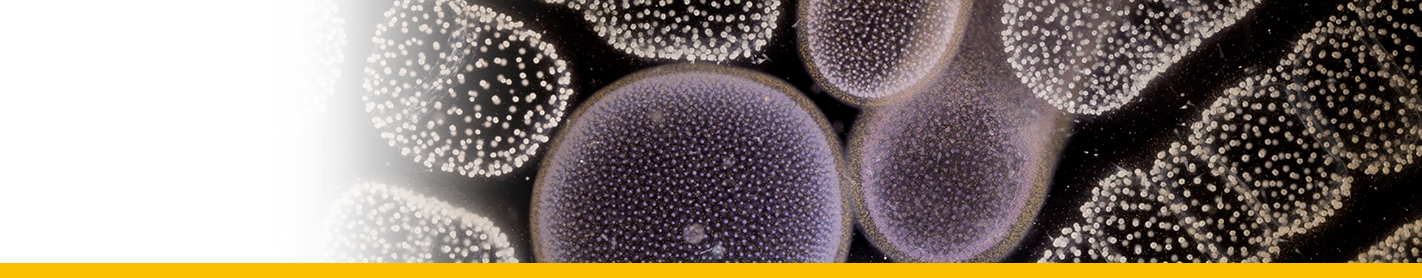
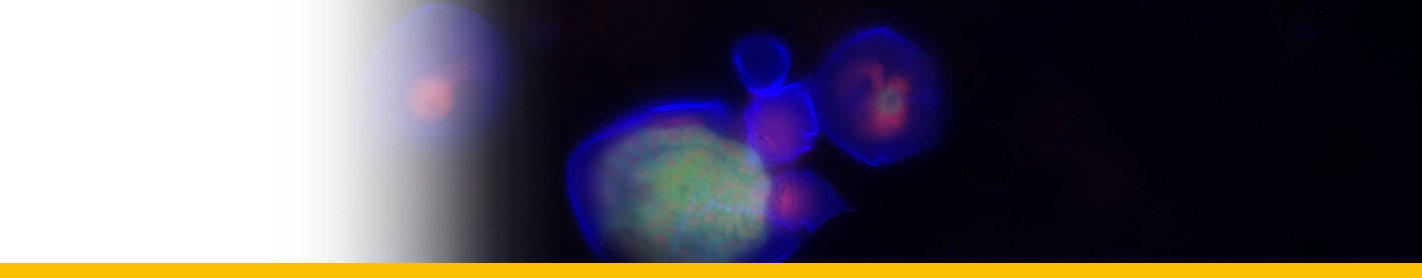
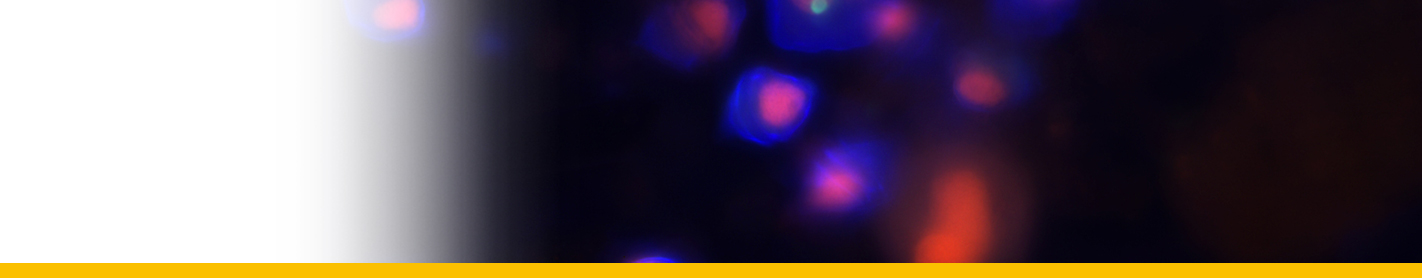
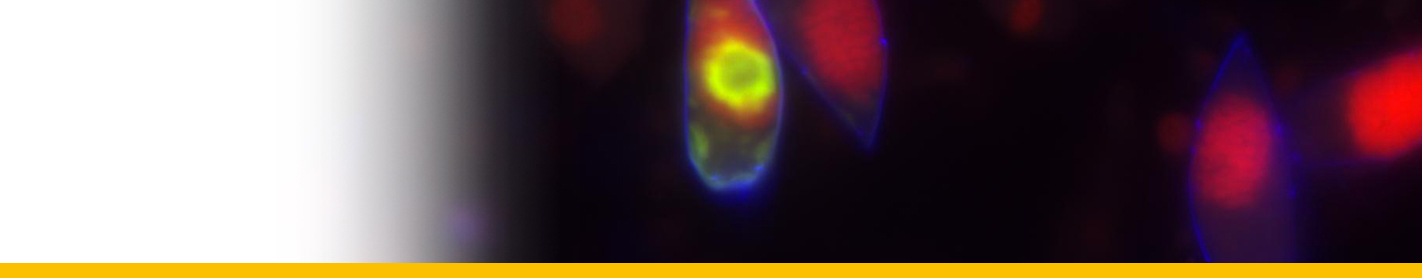
This species cannot be distinguished from A. tamarense by its shape. The primary difference from A. tamarense is the lack of the ventral pore. Cells are as long as wide or slightly longer then wide. Cell contains many golden brown elongated chloroplasts and a horseshoe-shaped nucleus located in the equatorial part of the cell. The epicone is helmet-shaped and the hypocone roughly trapezoidal. The cingulum is descending about one cingular height. The sulcus broadens in its antapical portion and is delimited on both sides by moderately developed sulcal lists. The cell surface is smooth and ornamented with many scattered small pores. The plate formula is: Po, 4’, 6’’, 5C, 8-10S, 5’’’, 2’’’’. Po is ornamented by several small pores and presents a comma-shaped foramen. A connecting pore is generally not present on Po. Plate 1’ is irregularly rhomboidal, with longer apical right and antapical left sides; in its apical portion, it contacts Po and in its antapical portion it contacts plate Sa. The ventral pore along the margin between Plate 1’ and 4’ is generally not present. Plate 6’’ is as wide as tall or slightly wider than tall. Plate 2’’’’ variable: it can be transverally extended (prevalent type) or dorsoventrally extended, but transitions exist. Plate sp is pentagonal, and its length:width ratio is ∼ 1; a connecting pore is generally not present on the sp plate. Cells are almost always single, rarely found in chains of two to eight cells in culture, but can be found in chains in the field. The cyst is ellipsoidal, with a granular dark brown content and is surrounded by a mucous layer. Isolates are almost always toxic (Lilly et al. 2007). The species is defined by the combined nucleotide sequences of the epitype strain SPE10-03 D1-D2 LSU (GenBank KF908807), ITS/5.8S (GenBank KF908818), and SSU (GenBank KF908795).
Body_length: 30-38 µm
Body_width: 30-38 µm
Etymology
Named after the Bay of Fundy, the type locality of A. fundyense Balech (Balech 1985).
Type species
The type strain SPE10-03
Type illustration / Type locality / Type specimen
Living cultures: RCC4086, CCMP3432. The type strain SPE10-03 was isolated from Salt Pond in Eastham, Massachusetts USA, 41.835 N 69.972◦ W on 05/12/2001 by K. Gribble.
Ecology
Substrate: planktonic
Sociability: solitary
Salinity: marine
pH: neutral
Feeding: Photosynthetic
Life cycle
Phases_alternance: haplontic
Generation: <1 month
Reproduction_mode: asexual_binary
Reproduction_mode: sexual_heterothallic
Resting_stage: cysts_sexual
Resting_stage: cysts_asexual