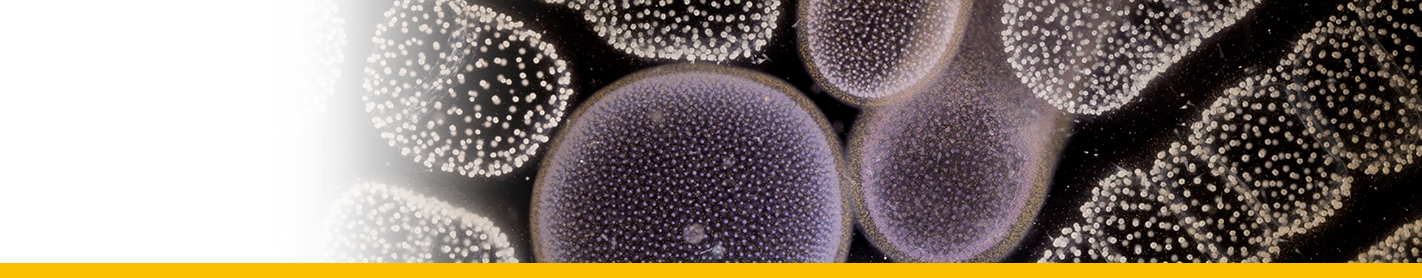
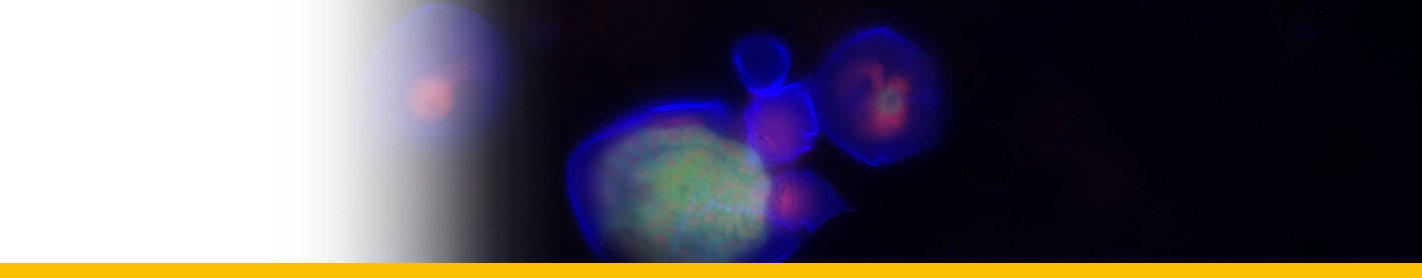
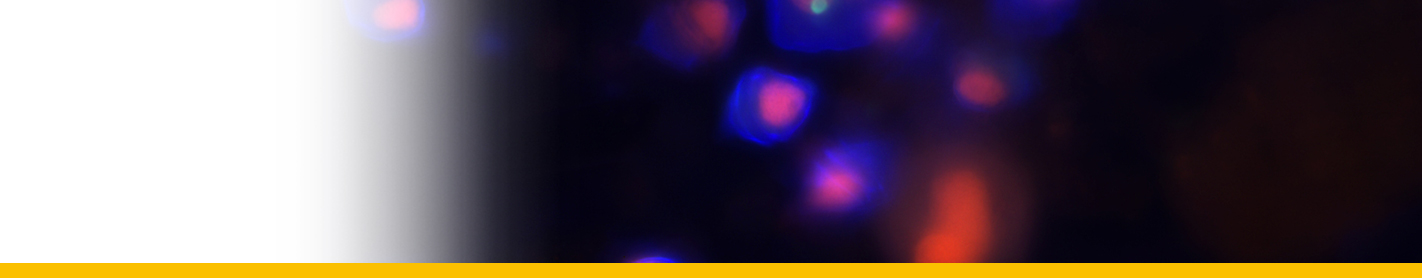
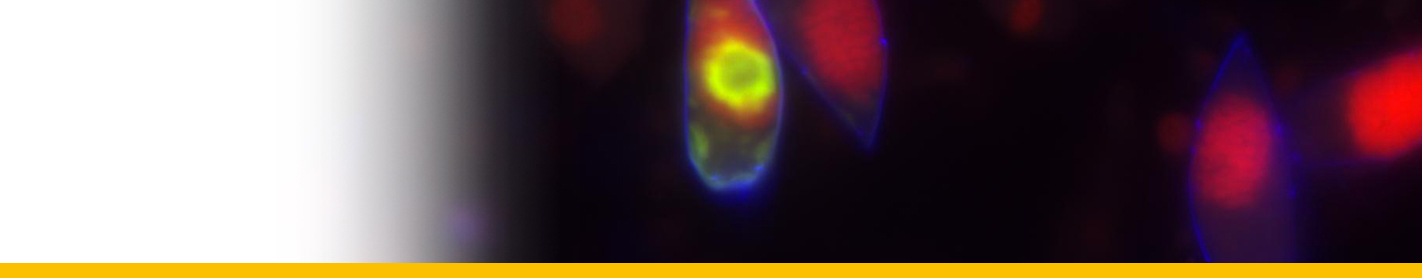
Levanderina fissa
Diagnosis
Diagnose_Species: Levanderina fissa. Unarmoured dinoflagellates with U-shaped apical groove surrounding the cell apex and opening on the ventral side of the cell. Apical groove with three rows of vesicles. Nuclear envelope without vesicular chambers. Nucleus connected to the flagellar apparatus via a finger-like projection. Chloroplasts present. The sulcus divided into an inner tube containing the longitudinal flagellum and an outer, open furrow. Cell division in the motile stage.
Bloom: No
Toxicity: No
Etymology
The genus is named after Prof. Kaarlo Mainio Levander (1867–1943), primus motor in marine plankton research in Finland. Prof. Levander found and described the type and presently only species of the genus.
Type species
This is the type species (holotype) of the genus Levanderina.
Type illustration / Type locality / Type specimen
Type locality= strain K-1769 from the type locality, Lövö, southern Finland, Baltic Sea near Helsinki.
Ecology
Substrate: planktonic
Sociability: solitary
Salinity: marine
pH: neutral
Feeding: Photosynthetic
Life cycle
Phases_alternance: haplontic
Generation: <1 month
Reproduction_mode: asexual_binary
Reproduction_mode: sexual
Resting_stage: cysts_sexual
Feeding behaviour
Mode of locomotion
Reference(s)
Attached phylogeny
Observation site(s)
SYMBIONTS
| Association with... | Region origin | Name of site | In reference... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amoebophrya ceratii-species complex | Chesapeake Bay |
(1996) Parasitism of photosynthetic dinoflagellates in a shallow subestuary of Chesapeake Bay, USA. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 11:1-9. |
|
| Amoebophrya ceratii-Clade-4 | Chesapeake Bay - Rhode river |
(2002) Multiple strains of the parasitic dinoflagellate Amoebophrya exist in Chesapeake Bay. J Eukaryot Microbiol 49:469-74. |